Blog
Stay up to date on the latest advances in regenerative medicine through our blog.

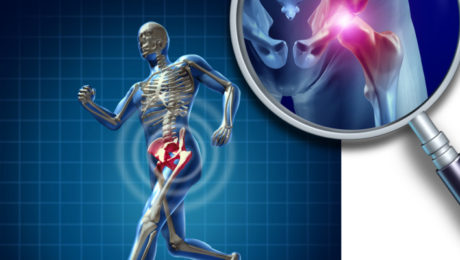
STANFORD RESEARCHERS ISOLATE SKELETAL STEM CELLS THAT GIVE RISE TO BONES AND CARTILAGE
Stanford Researchers Isolate Skeletal Stem Cells That Give Rise to Bones and Cartilage Cartilage and bone deterioration often result from aging, lifestyle factors, or injuries. Unlike bone tissue, mature cartilage has limited self-healing capabilities. Surgical interventions like joint replacement are costly and carry risks such as rejection and infection [1]. Stanford’s Breakthrough in Tissue Engineering
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
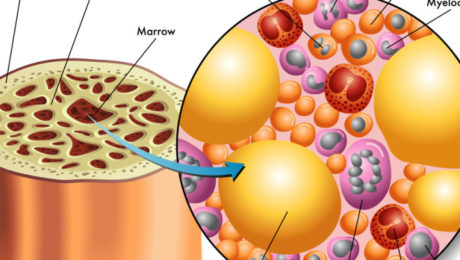
PROTEINS PRODUCED BY STEM CELLS, USED IN BONE REGENERATION
Bone loss and weakening are natural effects of aging, beginning as early as age 30. Factors like smoking, inadequate calcium intake, certain medications, and hormonal changes accelerate bone resorption, leading to decreased density, porous bones, and increased fracture risk. Stem Cell Innovations in Bone Reconstruction Researchers at the Gladstone Institutes have pioneered a method using
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
The different types of stem cells and their current uses
Stem cells possess remarkable potential in medical applications due to their ability to differentiate into diverse cell types and renew themselves. They play a crucial role in the body by generating specialized cells that form tissues such as muscles, bones, blood, and the brain. Types of Stem Cells Based on Origin Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
- Published in Corporate News / Blog

Get Our Company Presentation
DOWNLOAD NOW


Get Our Company Presentation
DOWNLOAD NOW
Facebook Posts
Problem displaying Facebook posts. Backup cache in use.
Type: OAuthException
The Regenerative Revolution is truly Global! ISSCA Portugal Conference has attendees from all
Over the world 🇵🇹🇵🇹🇵🇹🔥🔥🔥🔥
... See MoreSee Less
Facebook Posts
Problem displaying Facebook posts. Backup cache in use.
Type: OAuthException
The Regenerative Revolution is truly Global! ISSCA Portugal Conference has attendees from all
Over the world 🇵🇹🇵🇹🇵🇹🔥🔥🔥🔥
... See MoreSee Less
Send Us a Message
Contact Home GSCG website
Copyright © 2024 Stem Cells Group | All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions
CONTACT US
Datran Center 9100 S Dadeland Boulevard, Suite 1500. Miami Fl. 33156 United States
305-560-5337
info@stemcellsgroup.com