Regenerative medicine is the cutting-edge “medicine of the future,” offering the promise of efficacy by enabling human tissue to be repaired, replaced, and healed (regenerated) once it is damaged or diseased. These therapies supplement the body’s natural healing mechanisms, often employing stem cells to stimulate the renewal of tissue damaged by injury, disease, or age. The rapid expansion of scientific knowledge offers great promise for advances in this field, holding vast potential to improve the quality of human life.
What are Stem Cells?
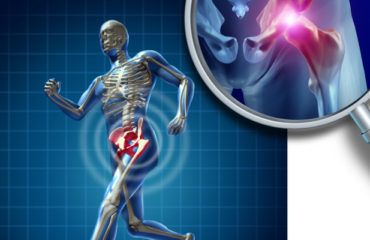
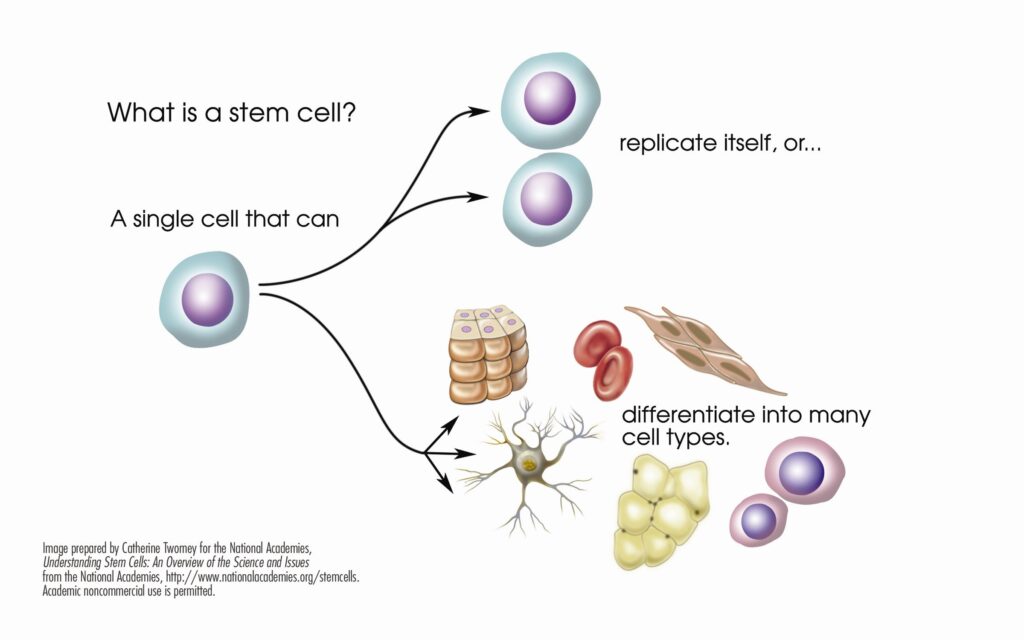
Stem cells are the basic building blocks of life. They are unspecialized cells capable of producing more stem cells through mitosis or differentiating into specialized cells that perform specific functions in the body. Stem cells are found throughout the body’s tissues, organs, and systems, although usually in small quantities in adults.
What are Hematopoietic Stem Cells?
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can give rise to all types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. They are particularly useful in treating blood-related diseases and conditions.
What are Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are multipotent stromal cells that are non-blood forming stem cells capable of differentiating into a variety of cell types, including muscle, bone, cartilage, and fat cells. When introduced into a patient’s body, MSCs can repair or replace damaged or degenerating tissue by communicating with surrounding cells, triggering a cellular cascade of healing (paracrine signaling).
The term MSC was coined in the late 1980s by Dr. Arnold Caplan of Case Western Reserve. Recently, Caplan redefined the acronym to “Medicinal Signaling Cell” to emphasize these cells’ role in secreting powerful bioactive molecules involved in cellular signaling and regeneration. Caplan now describes MSCs as a “multisite-regulatory dispensary” (Natural Drug Store).
The production of MSCs in the human body can be precipitated by bioactive placental tissues containing Growth Factors, Cytokines, and other powerful bioactive agents that trigger cell signaling. The remarkable ability of MSCs makes them irreplaceable in medical treatments.
What are Accessible Sources of Stem Cells?
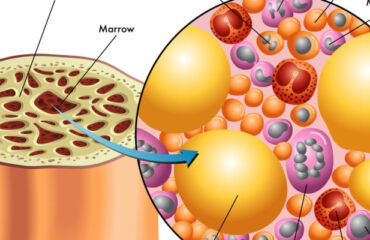
Stem cells can be extracted from various parts of the body, such as bone marrow and adipose tissue. More recently, birth tissues from live births, including umbilical cord blood, cord tissue with Wharton’s Jelly, and amniotic membrane tissue, have been found to be rich sources of both HSCs and MSCs. These tissues also precipitate the production of MSCs through paracrine signaling. Growth Factors, Cytokines, Exosomes, and micro-RNA from birth tissues give rise to stem cells in this way. These cells, as well as MSCs contained in Wharton’s Jelly, tend to be more fit than those obtained from adult stem cells.
Wharton’s Jelly
Wharton’s Jelly is a gelatinous substance found in the umbilical cord that is rich in stem cells. Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from Wharton’s Jelly have low immunogenicity. Human umbilical cord Wharton’s Jelly provides a new source for MSCs that are highly proliferative and have multi-differentiation potential. Wharton’s Jelly Cells (WJCs) express MSC markers but have low levels of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-ABC and no HLA-DR. WJCs have low functional immunogenicity, and recipient rejection has not been documented.
Advanced Regenerative Medicine
Advanced Regenerative Medicine involves the use of regenerative biomolecules, tissue engineering, and stem cells to treat diseased or injured tissues. This field leverages cutting-edge techniques to promote healing and regeneration, offering new hope for patients with previously untreatable conditions.