Engineering Stem and Stromal Cell Therapies for Musculoskeletal Tissue Repair
Musculoskeletal tissue injuries and degeneration are common and debilitating for a high number of patients (Brooks, 2006). Unfortunately, endogenous musculoskeletal tissue regeneration is limited in many cases and may be affected by inflammation and the degree of damage. For example, most fractures of long bones heal spontaneously, whereas large segmental defects fail to heal. Additionally, although articular cartilage has almost no intrinsic reparative potential, tendons and ligaments may heal, but often with inferior properties. The high prevalence of these injuries has led to significant investment in the development of new therapies to enhance healing and augment current surgical interventions. Often the goal is to mimic and recapitulate the natural healing cascade and developmental process by transplantation of tissue-specific stromal and progenitor cells or by endogenous manipulation to enhance the native repair capacity of cells.
Advances in Stem and Stromal Cell Therapies
There has been a continuing increase in the number and type of stem and stromal cells being pursued in human clinical trials for treatment of musculoskeletal injuries (Steinert et al., 2012). Most approaches in this area are based on ex vivo-expanded mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) derived from bone marrow (BM). Originally identified and characterized by their multilineage differentiation potential in vitro, multipotent capabilities of MSCs in vivo have not been clearly demonstrated to date, particularly because of the lack of methods to identify and define differentiated populations (Nombela-Arrieta et al., 2011). Central to recent progress in the field has been the understanding that stem and progenitor functions of MSCs may not be the key attribute that mediates tissue repair. In addition, there is outstanding controversy over the terminology of exogenously supplied MSCs as stromal cells, and various terms, including medicinal signaling cells, have been proposed to more accurately reflect their therapeutic function in vivo (Caplan, 2017). Nevertheless, the therapeutic benefit of these cells has been largely explored. Significant advances have been made in developing strategies that deliver, protect, and recruit stem cells, and the bioengineering field is evolving to improve current surgical techniques.
Current Treatments and Clinical Investigations
This review first describes current treatments and reports the recent progress in clinical investigations of stem and stromal cell-based therapies for musculoskeletal repair with a particular focus on bone and fibrocartilaginous tissues. The current understanding of appropriate cell sources and delivery strategies is then illustrated toward endogenous repair of musculoskeletal tissues. Last, emerging therapeutic concepts are highlighted in the context of biomaterials as a particularly attractive tool to control stem and stromal cell behavior both ex vivo and in vivo, to recruit endogenous stem cells, and to control the local healing environment. Such approaches have great potential for future therapies in musculoskeletal repair.
Bone Repair
The intrinsic repair of bone defects mirrors many events of embryonic development and makes fracture healing one of the rare postnatal processes that are regenerative and can ultimately restore damaged tissue to its pre-injury structure, composition, and biomechanical function (Figure 1). In spite of the unique capacity of bone to heal, a number of clinical indications remain where therapeutic intervention is required. In the case of complex trauma with multiple fractures, infections, and tumor-associated and endocrine diseases (e.g., diabetes, osteoporosis), the body’s natural healing response is impaired, and non-union can occur in up to 15% of cases (Grayson et al., 2015). Another debilitating disorder is non-traumatic avascular osteonecrosis, which can lead to collapse of the femoral head and accounts for 10,000–20,000 total hip replacement surgeries in the United States per year (Figure 1; Moya-Angeler et al., 2015). Autologous bone grafting represents the gold standard for management of bone defects and non-unions, and union rates of more than 90% have been reported using iliac crest bone. However, considerable donor site morbidity and limited volumes must be taken into consideration. Additionally, allogeneic or synthetic bone substitutes, such as ceramics, corals, or polymer-based materials, have not reached the biological and mechanical properties equivalent to autologous bone (Table 1).
Skeletal Muscle
In addition to direct traumatic injury, complex damage of bone tissue (e.g., open fractures, tumor ablations) often results in concomitant soft tissue injury, including adjacent muscles. Although skeletal muscle has the inherent ability to regenerate after injuries, the regenerative capacity fails when a large volume of muscle is lost (i.e., volumetric loss). Such severe injuries may lead to fibrosis, atrophy, and ischemia when left untreated, accounting for significant socioeconomic costs ($18.5 billion in healthcare costs are associated with sarcopenia alone) (Janssen et al., 2004). Therapeutic treatment options are limited to physical therapy, scar tissue debridement, and transfer of healthy, innervated, and vascularized autologous muscle tissue. However, the outcomes of surgical reconstructions often remain aesthetically and functionally deficient (Grogan et al., 2011; Table 1).
Articular Cartilage and Meniscus
In contrast to bone and skeletal muscle tissue, the poor intrinsic healing capacity of articular cartilage and meniscus tissue presents a major challenge in clinics. Lesions from injuries or degeneration often result in gradual tissue erosion, leading to impaired function of the affected joint and degenerative osteoarthritis (OA) (Figure 1). Patients with post-traumatic OA account for more than 10% of the 27 million adults in the United States that have a clinical diagnosis of OA (Johnson and Hunter, 2014). Commonly, the first-line treatment of articular injuries includes arthroscopic lavage, partial meniscectomy, and BM stimulation techniques to penetrate subchondral bone (Table 1). Microfracture has been considered the gold standard for stimulating endogenous repair; however, it often results in the formation of inferior fibrocartilaginous repair tissue. This cartilaginous tissue is vulnerable due to altered biomechanics of the subchondral bone, which raises concerns about the long-term efficacy of microfracture (Solheim et al., 2016). Therefore, secondary and more complex procedures strive to restore the hyaline cartilage, such as osteochondral autografting from the less weight-bearing periphery (mosaicplasty) and autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI). ACI represents one of the first clinical applications of tissue engineering where a biopsy from a low-weight-bearing region is performed, and ex vivo-expanded chondrocytes are implanted in a second operation. The de-differentiation of monolayer expanded chondrocytes and potential of recovery when implanted has been a matter of debate, and matrix-based ACI techniques have been developed that use absorbable scaffolds (e.g., porcine collagen) to support the implanted cells (Makris et al., 2015). An important limitation of these techniques is the long recovery time (6–12 months) to ensure neotissue formation. The choice of articular injury treatment depends on several factors, including localization and size of the lesion, the level of activity, and the degree of associated damage of menisci and ligaments.
Meniscus Repair
Tears of the fibrocartilaginous menisci require surgical intervention for nearly 1 million patients in the United States annually (Vrancken et al., 2013). For lesions located in the peripheral vascularized region of the meniscus, repair strategies such as sutures and anchors allow preservation of the meniscal tissue. However, meniscal lesions often appear in the avascular central regions, which makes them less suitable for healing and usually requires partial or (sub)total meniscectomy (Figure 1; Table 1). In some cases, further treatment with a meniscal substitute, such as an allograft or a synthetic implant, is indicated to limit OA (Vrancken et al., 2013).
Other Fibrous Musculoskeletal Tissues
Another large proportion of musculoskeletal injuries in the clinic is represented by other damaged fibrous structures, including tendons, ligaments, and the annulus fibrosus (AF). Often, degenerative pathology precedes acute trauma, and, like articular cartilage, these tissues have a limited healing capacity. One of the most common tendon injuries presented clinically is tearing of one or more of the interdigitating tendons of the rotator cuff (Figure 1). Failure of initial physical therapy or acute trauma in young patients motivates surgical repair using open or arthroscopic approaches for subacromial decompression, tendon debridement, and suture or anchor supplementation (Table 1). Still, repair is limited, particularly within the complex anatomic arrangement forming the shoulder cuff. The formation of fibrovascular scar tissue frequently leads to significant morbidity, re-ruptures, and difficulties in treatment choice.
The intervertebral discs (IVDs) are composed of the nucleus pulposus (NP), a hydrophilic proteoglycan-rich gelatinous core, surrounded by a dense fibrocartilage ring—the AF (Figure 1). The gradual progression of IVD degeneration and the extrusion of the NP through defects in the AF is a major cause for lower back pain, a leading cause of global disability (Sakai and Andersson, 2015). Available treatments are mostly symptomatic, and surgical treatments often resect the structural obstruction resulting from herniation or fuse motion segments (Table 1). However, the complex structural features of IVDs surrounded by neural elements and inflammation frequently cause a homeostatic imbalance favoring a catabolic response governed by the loss of the IVD structure, which is often followed by facet joint arthritis and vertebra deformation, canal stenosis, and even deformations. Most importantly, disc replacement with synthetic implants or fusion of the motion segment does not cure the underlying pathology of IVD degeneration (Sakai and Andersson, 2015).
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
ISSCA to Host Regenerative Medicine Symposium in Buenos Aires, Argentina August 24, 2018
Image: Facultad de Medicina – Universidad de Buenos Aires
ISSCA will host Applications of Cell Therapies in Medicine and Aesthetic Surgery, a regenerative medicine symposium in Buenos Aires, Argentina, August 24, 2018.
MIAMI, March 18, 2018—The International Association for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) has announced plans to host Applications of Cell Therapies in Medicine and Aesthetic Surgery, a regenerative medicine symposium. In Buenos Aires, Argentina August 24, 2018.
The international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift in healthcare from traditional to regenerative medicine in the 21st Century and provide cutting-edge information on developments in all areas of stem cell research. The Buenos Aires event will host a group of renowned international speakers in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will offer a day of rigorous scientific discourse aimed at physicians.
Topics of focus at the symposium include:
- Management of aging at the cellular level
- Stem cell therapies in medical aesthetics: the latest methods of harvest and isolation Non-invasive protocols of non-surgical facial and body rejuvenation
- Beyond fillers and toxins
- Combined treatment plans that include surgical methods for the management of advanced aging
- Restoration and assisted hair transplantation with biomaterials and growth factors
- The invaluable role of biological cosmeceutical in the management of aging
- The aging process from the inside out: the role of hormones
- Management of the latest digital marketing tools for recruiting patients in their aesthetic clinics
The symposium will incorporate the biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization of stem cells. Business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming these challenges will also be addressed.
The event will be held at the Facultad de Medicina – Universidad de Buenos Aires
To learn more about the ISSCA Buenos Aires symposium and to make a reservation, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About ISSCA:
 The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training. and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
ISSCA Buenos Aires Regenerative Medicine Symposium
- Published in Press Releases
ISSCA Founder Daeyong Kim, Ph.D., and Syed Salman Naeem Gilani, M.D. to speak at Istanbul Symposium
ISSCA Founder Daeyong Kim, Ph.D., and Syed Salman Naeem Gilani, M.D. to speak at the Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey, April 28, 2018.
MIAMI, March 18, 2018—ISSCA Founder and General Director Daeyong Kim, Ph.D., and Syed Salman Naeem Gilani, M.D. will be keynote speakers at the ISSCA Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018. Kim will discuss stem cell therapies for diabetes, and Gilani will speak on the effect of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells treatments on knee osteoarthritis.

Daeyong Kim, Ph.D.
Kim, a Global Stem Cells Group Advisory Board member, is an internationally recognized health educator, and CEO of N-Biotek, Inc, a preeminent manufacturer of biomedical and laboratory equipment and leader of stem cell technology solutions for providers worldwide.
Additionally, Kim is vice-president of BioChip Society, CEO of GTOP Construction Inc, managing director Woojoo Telecom, and managing director of KEPCO KDN.
In 2013, Kim completed an international business course at UC Berkeley, U.S. and received and an M.D. in alternative medicine at IBAM, India. In 2016, he received a Ph.D. in adipose-derived stem cell research at Westminster University in Korea.
Gilani is the Founder, CEO and Stem Cell/Regenerative Medicine Consultant for The Institute of Regenerative Medicine in Rawalpindi, Pakistan, the first-of-its-kind regenerative medicine institute in Pakistan that caters to clinical applications of stem cell and other regenerative medicine treatments. The institute also serves as a center of excellence in training physicians and paramedic staff in regenerative medicine in Pakistan.

Syed Salman Naeem Gilani, M.D.
In 2000, Gilani received his medical degree from Rawalpindi Medical College, Punjab University and completed a Fellowship in Stem Cell Therapy from the American Board of Anti-aging and Regenerative Medicine. He is ECFMG certified, a member of the American Academy of Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine, and a Diplomat of the American Academy of Aesthetic Medicine.
The Istanbul international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare solutions to regenerative medicine and provide the latest innovative discoveries and developments in all areas of stem cell research. The symposium will host a group of renowned international speakers, experts in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will provide a full day of rigorous scientific discourse directed to physicians.
The day’s events will incorporate information on stem cell biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization, business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming those challenges.
To participate in the ISSCA Istanbul Symposium, reserve your spot by registering today. For more information, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA):
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
Daeyong Kim, Ph.D., and Syed Salman Naeem Gilani, M.D.
- Published in Press Releases
R. Gökmen Turan M.D., Ph.D. and Mahir Mahirogullari, M.D. to speak at ISSCA Symposium in Istanbul April 28
ISSCA names R. Gökmen Turan M.D., Ph.D., and Mahir Mahirogullari, M.D. keynote speakers at the Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey, April 28, 2018.
MIAMI, March 18, 2018— R. Gökmen Turan M.D., Ph.D. and Mahir Mahirogullari, M.D. will be featured speakers at the ISSCA Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018. Turan will speak on therapeutic applications of stem cells in heart failure, and Mahirogullari will discuss cartilage treatment combining stem cells and biomedical scaffolds.

R. Gökmen Turan M.D., Ph.D.
Turan is a cardiologist and head of the Structural Heart Disease Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Porz Hospital, University Hospital of Cologne and University of Witten/Herdecke Germany.
Mahirogullari is an orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine and traumatology. He currently serves as a professor at Memorial Health Group in İstanbul, Turkey.
His focus includes multi-ligament injuries and cartilage repair of the knee; arthroplasty of the knee, hip and shoulder; arthroscopy of the knee, shoulder, hip, ankle and elbow joints; surgery of instability and cuff tear of the shoulder; orthopedic trauma, and the application of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), bone marrow aspirate stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells for treatment of orthopedic pathologies especially cartilage injuries.

Mahir Mahirogullari. M.D.
Mahirogullari received his medical degree (M.D.) from Gülhane Military Medical Academy School of Medicine in Ankara, Turkey in 1992 and completed his residency at GATA Haydarpasa Training Hospital in Istanbul.
He served as a general practitioner and orthopedic surgeon, treating and managing multi-trauma patients and war injuries. He also served with KFOR, NATO in Kosovo for six months. He worked as a Fellow with arthroscopic shoulder, knee, and trauma specialist Gary G. Poehling, M.D. in Winston Salem, North Carolina for one year before joining the faculty at Istanbul Medipol University School of Medicine in 2012 as chairman of the Department of Orthopedic Surgery. He has worked within the Memorial Health Group in Istanbul since 2016.
Mahirogullari is a member of The Turkish Society of Orthopedics and Traumatology (TOTBİD), The Turkish Society of Arthroscopy Knee Surgery & Orthopedics Sport Medicine (TUSYAD), The International Society of Arthroscopy Knee Surgery & Orthopedics Sport Medicine (ISAKOS), The Turkish Society of Shoulder and Elbow Society, The European Society of Sports Traumatology Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy (ESSKA 2000), The Turkish Board Certificate, and The Turkish Society of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty.
The Istanbul international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare solutions to regenerative medicine and provide the latest innovative discoveries and developments in all areas of stem cell research. The symposium will host a group of renowned international speakers, experts in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will provide a full day of rigorous scientific discourse directed to physicians.
The day’s events will incorporate information on stem cell biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization, business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming those challenges.
To participate in the ISSCA Istanbul Symposium, reserve your spot by registering today. For more information, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA):
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
R. Gökmen Turan M.D., Ph.D. and Mahir Mahirogullari, M.D.
- Published in Press Releases
ISSCA to Host New Stem Cell Training Course May 25-26, 2018 in Bogota, Colombia
Image: Bogota, Colombia
ISSCA will conduct the next hands-on regenerative medicine certification training course for physicians in Bogota, Colombia May 25-26, 2018.
MIAMI, Nov. 20, 2017—The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) announced plans to hold its next hands-on regenerative medicine certification training course for physicians in Bogota, Colombia May 25-26, 2018.
Plans for the next training workshop follow the success of the organization’s first Bogota-based course held March 2-3, 2018 and attended by eight physicians from three countries—Spain, Colombia, and Ecuador.
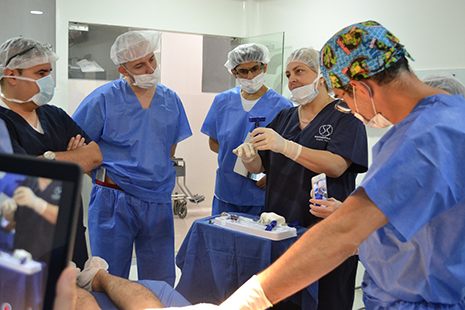
Stem cell training
The two-day, intensive training course teaches participating physicians how to harvest stem cells from adipose and bone marrow tissue. Participants learn while they conduct regenerative medicine protocols on live patients under the direction of stem cell training experts. Skills learned in the training course can be used to treat a variety of medical and aesthetic conditions such as osteoarthritis and facial rejuvenation.
Once certified, practitioners learn can use the techniques learned to treat patients in their practices and in clinical settings for career advancement. The course provides participating physicians with access to ISSCA’s online stem cell training course to review all content and procedures introduced during the two-day clinical training course, as well as patient forms and guidelines, procedures, informed consent forms, didactic lectures, training booklets, and more.
The ISSCA regenerative medicine protocols training course was developed for physicians and high-level practitioners to learn techniques in harvesting and reintegrating stem cells derived from patients’ adipose tissue and bone marrow.
Stem cell therapies continue to revolutionize the anti-aging aesthetics industry and help improve the quality of life for patients suffering from some chronic conditions.
Seating for this training course is limited. Register today to participate by visiting the Stem Cell Training Course Bogota website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call 305-560-5337.
About ISSCA:
 The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
Stem cell training Bogota
- Published in Press Releases
Mehmet Veli Karaaltın M.D. and Mehmet Bozourt, M.D. to speak at ISSCA Symposium in Istanbul April 28
ISSCA announces keynote speakers Mehmet Veli Karaaltın, M.D. and Mehmet Bozkurt, M.D. at the Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey, April 28.
MIAMI, March 18, 2018— Mehmet Veli Karaaltın M.D. and Mehmet Bozkurt, M.D. will be featured speakers at the ISSCA Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018. Karaaltın will speak on the role of cellular therapy and futuristic applications in plastic reconstructive surgery: from anti-aging to reconstructive surgery (level evidence IV). Bozkurt will discuss the application of regenerative cells on immunologic and diabetic wounds and severe burns.

Mehmet-Veli-Karaaltın, M.D.
Karaaltın, a Global Stem Cells Group advisory board member, specializes in head and maxillofacial surgery and hand surgery, and serves as an associate professor of plastic aesthetic & reconstructive surgery (European Board Certified) at Hacettepe University Medical Faculty in Ankara, Turkey.
After graduating from Istanbul University’s Cerrahpaşa English Medical Faculty, Karaaltın completed a national examination from Hacettepe University in Ankara, Turkey, placing 12th out of 25,000 doctoral candidates. He later completed all exam requirements of the European Society of Plastic Surgery. He is a member of the European Council of Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery and the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS).
In addition to his work in aesthetic applications, Karaaltın is also known for his work in microvascular free flaps, nerve transfers, facial surgery, and tissue transplants. He also practices cellular therapy and tissue regeneration for healing diabetic wounds, severe burns, and Buerger’s disease. He is one of only a few physicians in the world who offer surgical treatment for Lymphedema-Elephant Disease with microvascular lymph node transfer.

Mehmet Bozkurt, M.D.
Bozkurt is a plastic and reconstructive surgeon and serves as chairman and director of the plastic reconstructive surgery and burn center at Kartal Dr. Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital in Istanbul. He completed his clinical fellowship in microsurgery at Cleveland Clinic in 2012. Bozkurt is a member of The International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science, The İnternational Society of Burn Association, and The Turkish Aesthetic Surgery Association. He is board certified in European plastic surgery and Turkish plastic surgery.
He completed medical school in July 1995 at the Gulhane Military Medical Academy Faculty of Medicine in Ankara, Turkey and completed post-graduate studies and training in emergency medicine, microsurgery, plastic and reconstructive surgery, orthopedic medicine, and preventative medicine. He is the recipient of numerous honors and awards in his field.
The Istanbul international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare solutions to regenerative medicine and provide the latest innovative discoveries and developments in all areas of stem cell research. The symposium will host a group of renowned international speakers, experts in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will provide a full day of rigorous scientific discourse directed to physicians.
The day’s events will incorporate information on stem cell biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization, business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming those challenges.
To participate in the ISSCA Istanbul Symposium, reserve your spot by registering today. For more information, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA):
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
Mehmet Veli Karaaltın M.D. and Mehmet Bozourt, M.D.
- Published in Press Releases
Abdul Majeed M.D. and Hilmi Karadeniz, M.D. to speak at ISSCA Regenerative Medicine Symposium April 28
ISSCA announces keynote speakers Abdul Majeed, M.D. and Hilmi Karadeniz, M.D. at the Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey, April 28, 2018.
MIAMI, March 18, 2018—Abdul Majeed, M.D. and Hilmi Karadeniz, M.D. will be featured speakers at the ISSCA Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018. Majeed will discuss findings of a recent study on intra-arterial injection of autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells in ischemic stroke patients. Karadeniz will speak on current approaches to the application of regenerative treatments in athletes.

Abdul Majeed, M.D.
Majeed is a hematologist, consultant, FRCP London, and a pioneer in stem cell transplantation and stem cell therapies in Iraq. He heads Global Stem Cells Group affiliate Stem Cell Centre in Baghdad. In 1992, he obtained a degree from the Board of Internal Medicine and served as the head of the medicine department Bin Majid hospital in Basra, southern Iraq.
In 2004, Majeed invited Prof. Marino Andolina (a pediatric immunologist from Trieste Italy) to Baghdad to perform the first autologous bone marrow transplant in Iraq. In 2009, Majeed and his team in Iraq began providing bone marrow-derived stem cell therapy for spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, and other medical conditions. He served as director of the bone marrow transplantation unit at the medical city hospital in Baghdad from 2011 to 2017.

Hilmi Karadeniz, M.D.
Karadeniz specializes in orthopedics and traumatology including sports medicine and surgery, arthroplasty, trauma surgery, spinal surgery, and ultrasound-guided PRP applications.
He studied at Istanbul School of Medicine, Istanbul University from 1998 – 2004, and Orthopedics and Traumatology Clinic II, Istanbul Research and Training Hospital, Ministry of Health from 2005 – 2011. Karadeniz currently serves as an orthopedic surgeon and traumatologist at Şişli Kolan Hospital in Istanbul.
The Istanbul international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare solutions to regenerative medicine and provide the latest innovative discoveries and developments in all areas of stem cell research. The symposium will host a group of renowned international speakers, experts in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will provide a full day of rigorous scientific discourse directed to physicians.
The day’s events will incorporate information on stem cell biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization, business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming those challenges.
To participate in the ISSCA Istanbul Symposium, reserve your spot by registering today. For more information, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA):
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
Abdul Majeed, M.D. and Hilmi Karadeniz, M.D.
- Published in Press Releases
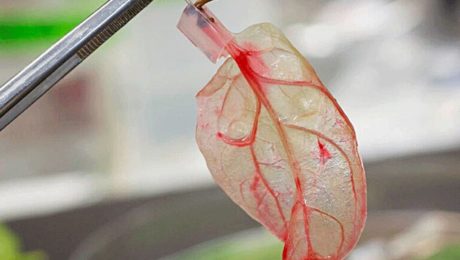
Vascular Tissue Engineering: Progress, Challenges, and Clinical Promise
Introduction
The clinical demand for bioengineered blood vessels continues to rise, yet current options for vascular conduits remain limited. The synergistic combination of emerging advances in tissue fabrication and stem cell engineering promises new strategies for engineering autologous blood vessels that recapitulate not only the mechanical properties of native vessels but also their biological function. Here, we explore recent bioengineering advances in creating functional blood macro and microvessels, particularly featuring stem cells as a seed source. We also highlight progress in integrating engineered vascular tissues with the host after implantation and the exciting pre-clinical and clinical applications of this technology.
The Clinical Need for Vascular Grafts
Ischemic diseases, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD), remain one of the leading causes of mortality and morbidity worldwide (GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators, 2016; Mozaffarian et al., 2016). These diseases have resulted in an ever-persistent demand for vascular conduits to reconstruct or bypass vascular occlusions and aneurysms. Synthetic grafts for replacing occluded arterial vessels were first introduced in the 1950s following surgical complications associated with harvesting vessels, the frequent shortage of allogeneic grafts, and immunologic rejection of large animal-derived vessels. Despite advances in pharmacology, materials science, and device fabrication, these synthetic vascular grafts have not significantly decreased overall mortality and morbidity (Nugent and Edelman, 2003; Prabhakaran et al., 2017).
Challenges with Synthetic Grafts
Synthetic grafts continue to exhibit a number of shortcomings that have limited their impact. These shortcomings include low patency rates for small diameter vessels (< 6 mm in diameter), a lack of growth potential for the pediatric population necessitating repeated interventions, and susceptibility to infection. Vascular conduits are also needed for clinical situations such as hemodialysis, which involves large volumes of blood that must be withdrawn and circulated back into a patient several times a week for several hours.
The Importance of Microvascularization
In addition to large-scale vessel complications, ischemic diseases also arise at the microvasculature level (< 1 mm in diameter), where replacing upstream arteries would not address the reperfusion needs of downstream tissues (Hausenloy and Yellon, 2013; Krug et al., 1966). Microvascularization has proven to be a critical step during regeneration and wound healing, where the delay of wound perfusion (in diabetic patients, for example) significantly slows down the formation of granulation tissue and can lead to severe infection and ulceration (Baltzis et al., 2014; Brem and Tomic-Canic, 2007; Randeria et al., 2015).
Structural Components of Blood Vessels
To design advanced grafts, it is important to consider the structural components of a blood vessel. Many different blood vessel beds share common structural features. Arteries, veins, and capillaries have a tunica intima comprised of endothelial cells (EC), which regulate coagulation, confer selective permeability, and participate in immune cell trafficking (Herbert and Stainier, 2011; Potente et al., 2011). Arteries and veins are further bound by a second layer, the tunica media, composed of smooth muscle cells (SMC), collagen, elastin, and proteoglycans, conferring strength to the vessel and acting as effectors of vascular tone. Vascular tissue engineering has evolved to generate constructs that incorporate the functionality of these structural layers, withstand physiological stresses inherent to the cardiovascular system, and promote integration in host tissue without mounting immunologic rejection (Chang and Niklason, 2017).
Suitable Cell Sources
A suitable cell source is critical to help impart structural stability and facilitate in vivo integration. Patient-derived autologous cells are one potential source that has garnered interest because of their potential to minimize graft rejection. However, isolating and expanding viable primary cells to a therapeutically relevant scale may be limited, given that patients with advanced arterial disease likely have cells with reduced growth or regenerative potential. With the advancement of stem cell (SC) technology and gene editing tools such as CRISPR, autologous adult and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are emerging as promising alternative sources of ECs and perivascular SMCs that can be incorporated into the engineered vasculature (Chan et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2017).
Engineering and Integration of Vascular Tissues
A viable cell source alone is not sufficient for therapeutic efficacy. Although vascular cells can contribute paracrine factors and have regenerative capacity, merely delivering a dispersed mixture of ECs to the host tissue has shown limited success at forming vasculature or integrating with the host vasculature (Chen et al., 2010). Recent tissue engineering efforts have focused on recreating the architecture and function of the vasculature in vitro before implantation, with the hypothesis that pre-vascularized grafts and tissues enhance integration with the host.
Clinical Applications
The first reported successful clinical application of tissue-engineered blood vessels (TEBV) in patients was performed by Shin’oka et al., who implanted a biodegradable construct as a pulmonary conduit in a child with pulmonary atresia and single ventricle anatomy (Shin’oka et al., 2001). The construct was composed of a synthetic polymer mixture of L-lactide and e-caprolactone, reinforced with PGA, and seeded with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs). The authors demonstrated patency and patient survival 7 months post-implant, and expanded their study to a series of 23 implanted TEBVs and 19 tissue patch repairs in pediatric patients (Hibino et al., 2010). They reported no graft-related mortality, and four patients required interventions to relieve stenosis at a mean follow-up of 5.8 years.
The first sheet-based technology to seed cultured autologous cells, developed by L’Heureux et al., induced cultured fibroblast cell sheets over a 10-week maturation period to produce tubules of endogenous ECM over a production time ranging between 6 and 9 months. They dehydrated and provided a living adventitial layer before seeding the constructs with ECs (L’Heureux et al., 2006). Their TEBV, named the Lifeline graft, was implanted in 9 of 10 enrolled patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis and failing access grafts in a clinical trial. Six of the nine surviving patients had patent grafts at 6 months, while the remaining grafts failed due to thrombosis, rejection, and failure (McAllister et al., 2009).
Future Directions
Harnessing the regenerative functions reported in ECs derived from adult stem cells and iPSCs offers the promise of improving TEBV patency. Mcllhenny et al. generated ECs from adipose-derived stromal cells, transfected them with an adenoviral vector carrying the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene, and seeded the ECs onto decellularized human saphenous vein scaffolds (McIlhenny et al., 2015). They hypothesized that through inhibition of platelet aggregation and adhesion molecule expression, nitric oxide synthesis would prevent thrombotic occlusion in TEBV. Indeed, they reported patency with a non-thrombogenic surface 2 months post-implantation in rabbit aortas. Engineering ECs and SMCs with other regenerative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-thrombotic genes could bridge the functional difference between SC-derived cells and native primary cells.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
MIAMI, Feb 19, 2018—Amine Rafik, M.D., Ph.D., a member of the Global Stem Cells Group Advisory Board, will be a keynote speaker at the International Association for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018. Rafik will speak on the role of adipose-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine as an attractive alternative to the use of stem cells derived from bone marrow and other sources, due to their abundance in fat and their ability to be easily harvested.

Amine Rafik, M.D., Ph.D
Rafik will present a retrospective review of patients treated for leg ulcers with lipofilling between 2011 – 2014 at the National Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, University Hospital. Ibn-Rochd Casablanca, Morocco.
Rafik’s lecture will include patient demographic data and digital photographs taken on the day of each patient’s surgery and every day thereafter. ASC patients received three treatments of 20 cc of autologous adipose stem cell injections in the subcutaneous tissue surrounding the ulcer with time to wound closure defined as the time at which the wound bed was completely re-epithelialized and filled with new tissue.
He will discuss study results revealing the average time for wound closure in adipose stem cell (ASC) recipient patients compared to control group patients. He will also examine the study’s conclusion that suggests local transplantation of autologous adipose stem cells could accelerate wound healing, and that some clinical aspects of wound healing, as well as the potential for therapies based on stem cells, represent a feasible therapeutic approach to the treatment of clinical wounds.
Rafik is a consultant and plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgeon at Al Farabi Hospital in Morocco. He specializes in reconstructive plastic surgery particularly for the face, head, and neck, as well as for patients who require reconstructive surgery following treatment for skin cancer or trauma. Rafik also performs cosmetic surgery and microsurgery.
He completed his plastic surgery training in Casablanca and was awarded full membership to the American Academy of Cosmetic Surgery in 2015, and the European Association of Maxilla-Facial surgery in 2016.
He is a reviewer for many international indexed journals, including; OncoTargets and Therapy Journal, the British Journal of Medicine and Medical Research, and the Cancer and Clinical Oncology Journal, published by Canadian Center of Science and Education, where he is a member of the editorial board.
The Istanbul international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare solutions to regenerative medicine and provide the latest innovative discoveries and developments in all areas of stem cell research. The symposium will host a group of renowned international speakers, experts in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will provide a full day of rigorous scientific discourse directed to physicians.
The day’s events will incorporate information on stem cell biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization, business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming those challenges.
To participate in the ISSCA Istanbul Symposium, reserve your spot by registering today.
For more information, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA):
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
ISSCA conference speaker Amine Rafik
- Published in Press Releases
ISSCA to Host Regenerative Medicine Cell Therapies Symposium at Hotel Hyatt Regency, Istanbul, Turkey
ISSCA Istanbul conference: The International Association for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) has announced plans to host a regenerative medicine symposium at the Hotel Hyatt Regency in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018.
MIAMI, Feb 19, 2018—The International Association for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) will host its next regenerative medicine symposium at the Hotel Hyatt Regency in Istanbul, Turkey April 28, 2018.
The symposium agenda will focus on:
- Molecular biology
- Clinical advances in stem cell research
- Models of treatment in surgical and cosmetic applications, and in clinical conditions
- Technological advances
- Application of minimally manipulated stem cells in the physician’s office
- Stem cells, regenerative medicine and its application in anti-aging medicine, Pain Management and Orthopedics
- Medical legal issues.
- Regulatory Pathways
Istanbul, the economic, cultural, and historic center of Turkey, is the country’s most populous city. The luxurious Hotel Hyatt Regency, located near Istanbul’s Ataturk Airport, offers visitors the combination of comfort, culture, and convenience for exploring the ancient city. Symposium attendees will be able to discover sights such as the Blue Mosque and the Hagia Sophia.
The Istanbul international symposium is part of ISSCA’s mission to support a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare solutions to regenerative medicine, and provide the latest innovative discoveries and developments in all areas of stem cell research. The symposium will host a group of renowned international speakers, experts in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine, who will provide a full day of rigorous scientific discourse directed to physicians.
The day’s events will incorporate information on stem cell biology, medicine, applications, regulations, product development, and commercialization, business opportunities, challenges, and potential strategies for overcoming those challenges.
To participate in the ISSCA Istanbul Symposium, reserve your spot by registering today.
For more information, visit the stemcellconference.org website, email info@stemcellsgroup.com, or call +1305 560 5337.
About International Society for Stem Cells Applications
The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) is a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians, all of whom aspire to treat diseases and lessen human suffering through advances in science, technology and the practice of regenerative medicine. ISSCA serves its members through advancements made to the specialty of regenerative medicine.
The ISSCA’s vision is to take a leadership position in promoting excellence and setting standards in the regenerative medicine fields of publication, research, education, training, and certification.
As a medical specialty, regenerative medicine standards and certifications are essential, which is why ISSCA offers certification training in cities all over the world. The goal is to encourage more physicians to practice regenerative medicine and make it available to benefit patients both nationally and globally. Incorporated under the Republic of Korea as a non-profit entity, the ISSCA is focused on promoting excellence and standards in the field of regenerative medicine.
###
ISSCA Istanbul conference
- Published in Press Releases